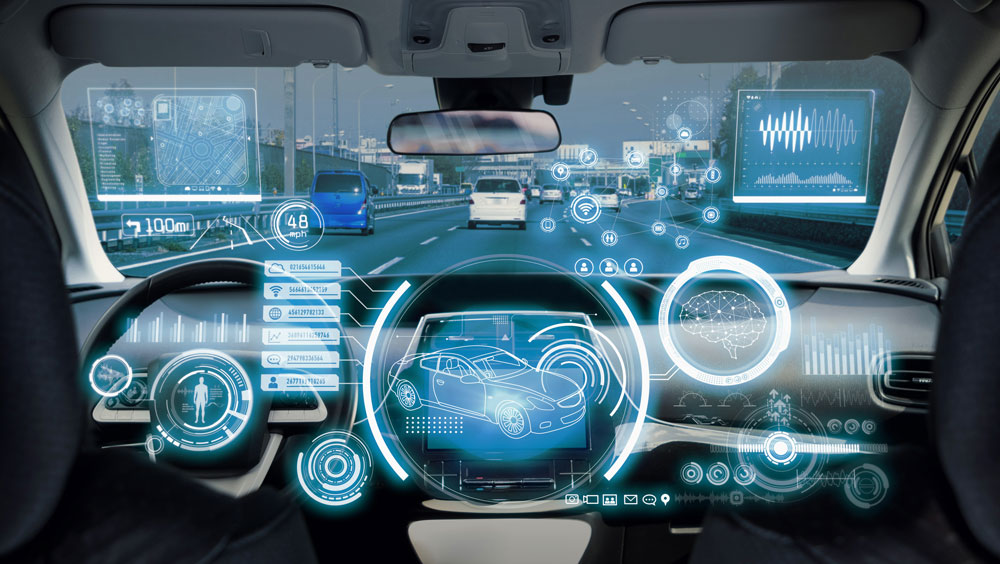

Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are groups of electronic technologies that assist drivers in driving and parking functions. Through a safe human-machine interface, ADAS increase car and road safety. ADAS use automated technology, such as sensors and cameras, to detect nearby obstacles or driver errors, and respond accordingly.
How are ADAS systems used in a car?
These systems react faster than any human, are constantly vigilant, and are already being adopted and deployed across various car segments, from premium to economy models. ADAS systems constantly monitor the vehicle surroundings, alert the driver of hazardous road conditions, and take corrective actions, such as slowing or stopping the vehicle.
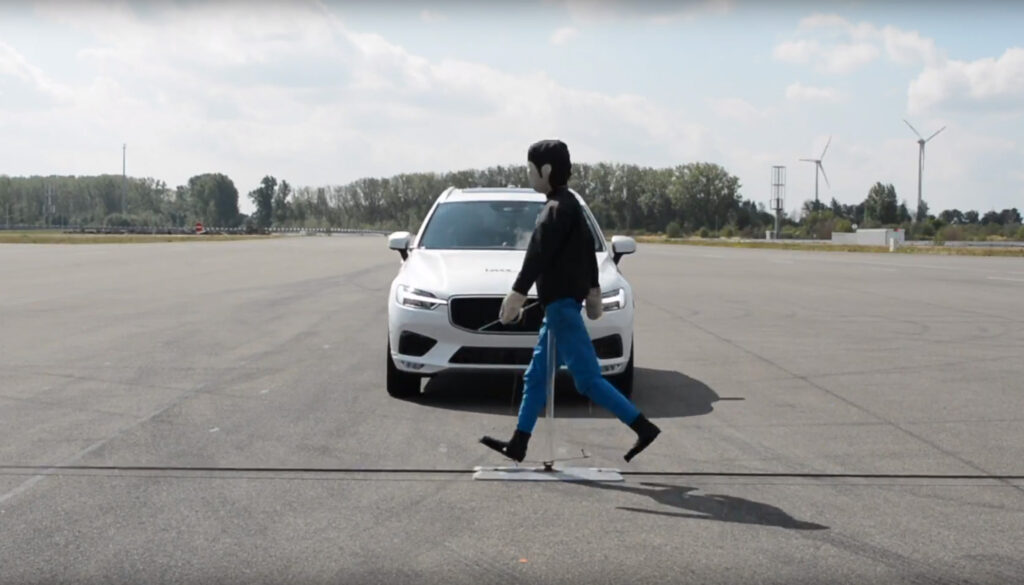

Levels of ADAS
ADAS are categorized into different levels based on the amount of automation, and the scale provided by The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). ADAS can be divided into five levels. In level 0, ADAS cannot control the car and can only provide information for the driver to interpret on their own.

Some ADAS that are considered level 0 are: parking sensors, surround-view, traffic sign recognition, lane departure warning, night vision, blind spot information system, rear-cross traffic alert, and forward-collision warning. Level 1 and 2 are very similar in that they both have the driver do most of the decision making. The difference is level 1 can take control over one functionality and level 2 can take control over multiple to aid the driver.

ADAS that are considered level 1 are: adaptive cruise control, emergency brake assist, automatic emergency brake assist, lane-keeping, and lane centering.ADAS that are considered level 2 are: highway assist, autonomous obstacle avoidance, and autonomous parking. From level 3 to 5, the amount of control the vehicle has increases; level 5 being where the vehicle is fully autonomous. Some of these systems have not yet been fully embedded in commercial vehicles. For instance, highway chauffeur is a Level 3 system, and automatic valet parking is a level 4 system, both of which are not in full commercial use yet.

Feature examples of ADAS
- Adaptive cruise control
- Anti lock bracking system (ABS)
- Automatic parking
- Automotive heads up display
- Automotive navigation system
- Automotive night vision
- Back-up camera
- Blind spot monitor
- Cruise control
- Emergency driver assistance
- Hill descent control
- Hll start assist, and many others.
- Adaptive cruise control
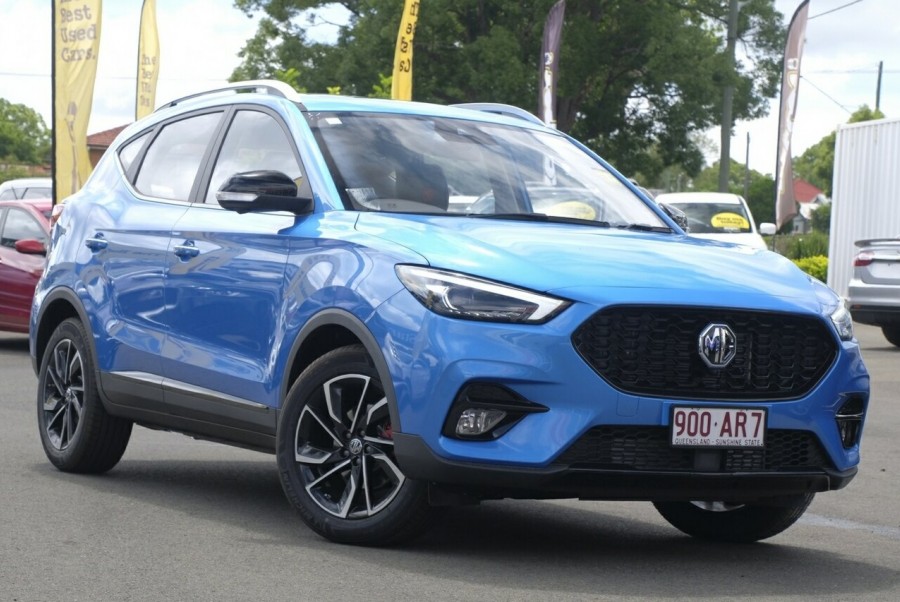

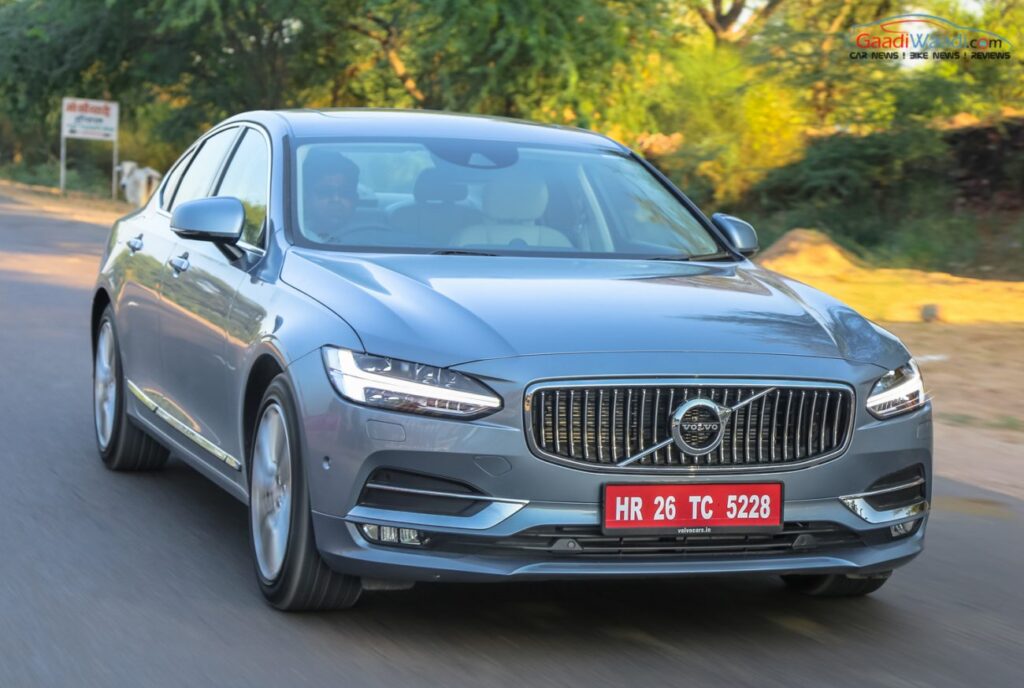
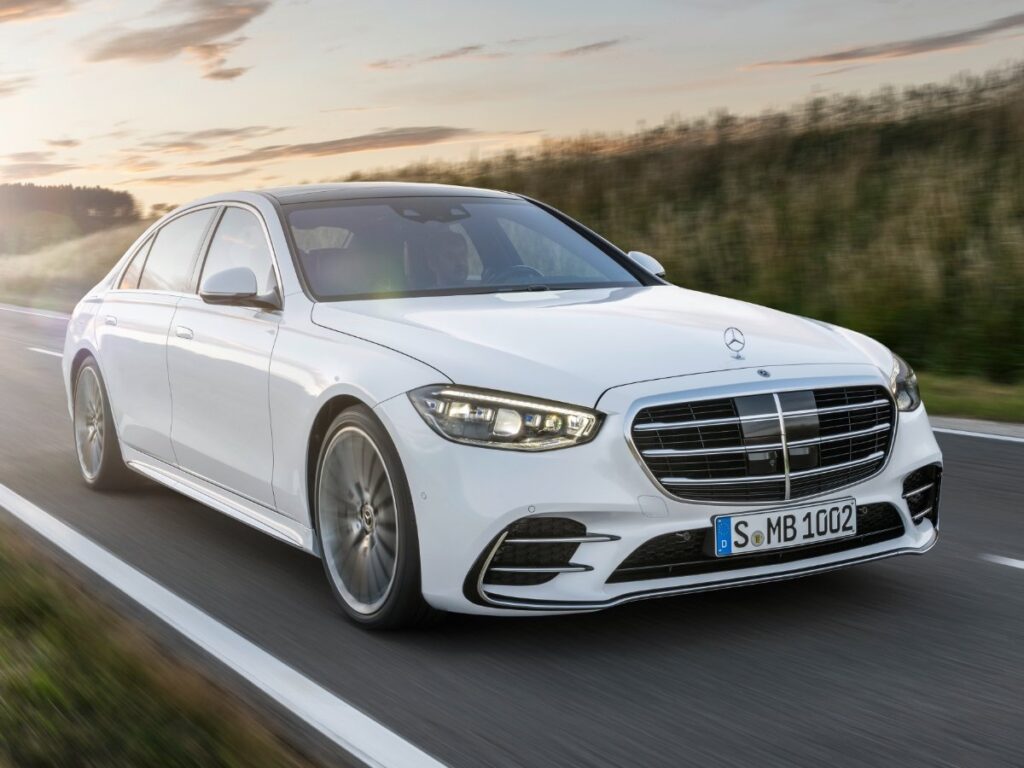
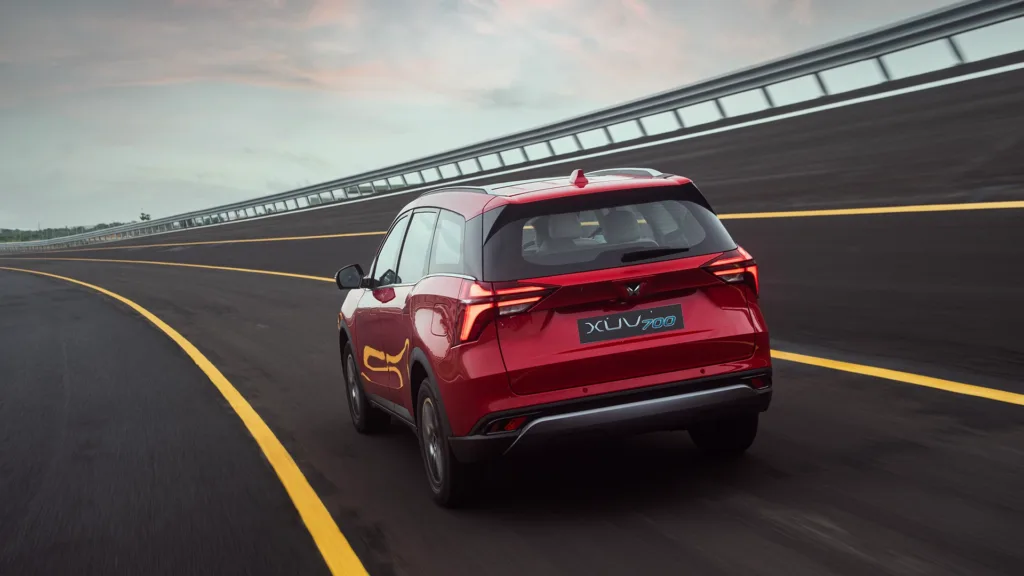
Popoular cars in india that have ADAS
- MG Gloster
- MG Astor
- Mahindra XUV 700
- VOLVO cars, including XC40, XC60, XC90, S60, S90, etc
- Mercedes Benz S class, and many other cars in the continuation of this range.

What do you need to know about Adas in cars?

ADAS is the essential step between initial Driver Assistance (DA) systems and fully autonomous cars, and typical solutions include various digital sensors such as RADAR, LIDAR and digital CMOS cameras to capture, fuse and process data from the vehicle driving environment.

